Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment in Pune
Rheumatoid arthritis treatment in pune (RA) is used to treat a common form of arthritis that causes inflammation within the lining of the joints, reduced range of motion, swelling and pain. RA tends to persist for several years, which often affects multiple joints of the body and may also cause damage to cartilage, bones, tendons and ligaments of the joints.
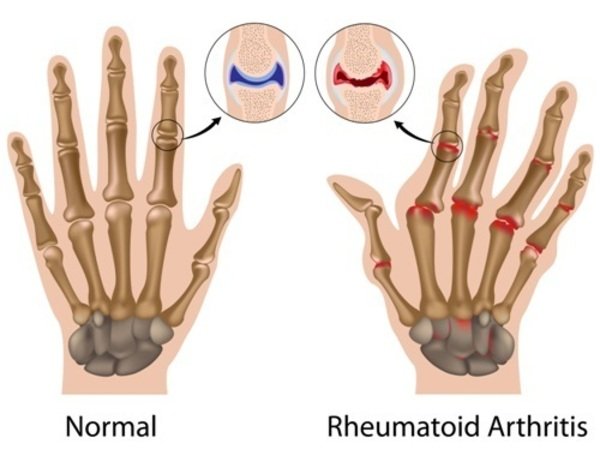
What differentiates rheumatoid arthritis from other forms of arthritis?
One way to differentiate RA from other kinds of arthritis is by the pattern of the affected joints. for instance, RA affects the wrist and small joints of the hand (MCPs and PIPs) but, normally, doesn’t affect the joints that are closest to the nails (DIPs). Conversely, osteoarthritis, a more common kind of arthritis, most frequently affects joints closer to the nails than other areas of the hand.
Joints Mostly Affected by Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) include:
- Wrists and small joints of hands and feet
- Elbows
- Shoulders
- Knees
The spine is typically not affected by Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), except the neck. Another essential feature of RA is that the joints on either side of the body tend to be affected. Like to mention if the knuckles of the right hand are inflamed, probably, the same knuckles of the other hand might also be inflamed.
The general pattern of the affected joints, along with certain symptoms allows the rheumatoid arthritis specialist doctor to easily differentiate RA from other conditions.
The reasons behind RA are unknown; however, the body’s immune system plays a vital role in the inflammation and damage that RA causes within the joints. In RA, the immune system attacks the body’s joints and might also affect other organs of the body. It is also observed that in RA, the cells of the body’s system invade the tissues of the joints and cause inflammation. These cells within the tissue and fluid of the joint produce many substances, including enzymes, antibodies and cytokines, which attack the joint and may damage it.
What are the Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
The symptoms of RA vary from one person to another. In some people, the disease may be mild, with periods of activity (in which the inflammation of the joints worsens) called periods of exacerbation. In others, the disease remains active continuously and worsens, or progresses with the passage of your time.
If you have RA, you’ll feel the subsequent symptoms in some joints:
- Swelling
- Redness
- Frequent pain
- Difficulty in mobility
These physical signs of arthritis are caused by inflammation of the lining, or synovium, of the joints. If this inflammation persists or doesn’t respond well to treatment of arthritis, it can further damage adjacent cartilage, bone, tendons and ligaments, resulting in deformities of the joints.
Rheumatoid arthritis can make you feel completely sick, particularly in periods of aggravation and you could:
- Lose your appetite
- Lose weight
- Have low energy
- Present fever of low temperature (febrile)
- Become anaemic
- Develop rheumatoid nodules (lumps of tissue that form under the skin)
Rheumatoid arthritis can affect different parts of a joint, such as:
- The membrane
- The joint capsule
- Bone
- The muscle
- The tendon
- Synovial fluid
- The cartilage
Often rheumatoid nodules are formed over bony areas exposed to pressure. These are often found around the elbow, and also in other parts of the body, like the fingers, spine or feet.
RA also affects other organs of the body like:
- The linings that surround the heart (pericarditis) and also the lungs (pleuritis).
- Lung tissue
- Tear glands and salivary glands (syndrome of sica / dryness or Sjogren’s syndrome)
- Blood vessels (vasculitis)
How is Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnosed?
Clinical history and physical examination make it easy to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis.
To diagnose RA, your rheumatoid arthritis doctor will take your case history and perform a physical exam. He will search for certain characteristics of RA and he might also ask if you’ve experienced fatigue or a general feeling of stiffness, especially when getting up within the morning since these two symptoms are related to RA.
Your might also advise you to get some tests done:
- Blood Test
You might be recommended some blood tests. Tests detect the presence of Rheumatoid factor (‘RA factor’) and Anti-CCP in the blood. Other abnormalities that are discovered through laboratory tests include anaemia and a high rate of erythrocyte sedimentation (ESR) or C-reactive protein (CRP), which indicate the presence of inflammation.
Although these blood tests could also be useful in establishing a diagnosis, there’s no single test that will establish or exclude the diagnosis of RA.
- X-rays
Radiographs of hand and feet are useful to track joint damage which occurs in patients with progressive disease. Among the results that sometimes suggest the presence of RA include:
- Bone loss within the margins of the joint called erosions
- Loss of articular cartilage
With recent advances in management of RA there are a variety of treatments options available. A rheumatologist is an expert in this disease and should be consulted early in the course of the illness. Therapies used by the rheumatoid arthritis specialist doctor can slow and, in some cases, stop the disease. It is a misconception that allopathy doctors only prescribe steroids and painkillers. He might prescribe disease-modifying medications to help with symptoms and stop the progression of the disease. Newer therapies (Biologics treatment in pune) used by the rheumatologist can slow and, in many cases, stop the disease progression. Simple painkillers will not prevent joint damage. The emphasis of current treatment approaches is on:
- Reduce inflammation and relieve pain
- Prevent or delay joint damage
- Improve the functions and well-being of patients
Biological Therapies
There have been significant advances in treating rheumatoid arthritis, especially for patients whose arthritis does not respond to traditional disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) like methotrexate, sulfasalazine etc. The most important advance has been the development of a group of drugs called biologics. The newer, second-generation biologics have come to market only in the past 10 to 15 years or so. Other names for biologic therapies include: biologic agents, biologics, biological response modifiers or immunotherapy.
Biologics are a class of drugs that target specific parts of the immune system. With RA, the immune system goes into overdrive and attacks healthy cells. So, bringing the immune system under control is key to managing the disease.
It is now clear that the first year is a critical time to treat RA. Often much of the bone and joint damage starts early, within a few months of onset. Biologics have given new hope to people with rheumatoid arthritis. They are considered a possible treatment for patients who have uncontrolled RA despite the use of DMARDs. Biologics have been shown to help slow progression of rheumatoid arthritis when all other treatments have failed. Biologics do not reverse existing damage, but can protect the joints against continued damage. Aggressive rheumatoid arthritis treatment in Pune is known to help prevent disability. Biologics have revolutionized the treatment of various other diseases such as psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, Crohn’s disease and are widely used in treating a variety of cancers.
Biological therapies are newer drugs that are derived from living organisms and may be produced by biotechnology methods. In contrast most drugs are essentially chemicals synthesized from other chemicals. Biologics are used to treat moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis that has not responded adequately to other treatments. They differ significantly from traditional drugs used to treat rheumatoid arthritis in that they target specific components of the immune system instead of broadly affecting many areas of the immune system.
Some biological therapies are called anti-TNF drugs. They target a protein called tumour necrosis factor (TNF), which increases inflammation when excess amounts are present in the body. Other biological therapies target different proteins. Biological therapies are only given to people who haven’t responded to conventional DMARDs or who’ve had side-effects from them.
At Apex Clinic – Dr. Pravin Patil a rheumatoid arthritis specialist doctor in Pune provides treatment of arthritis taking into account the seriousness of your arthritis, other health conditions and your lifestyle. We ensure to provide the most effective plan of treatment for you.
